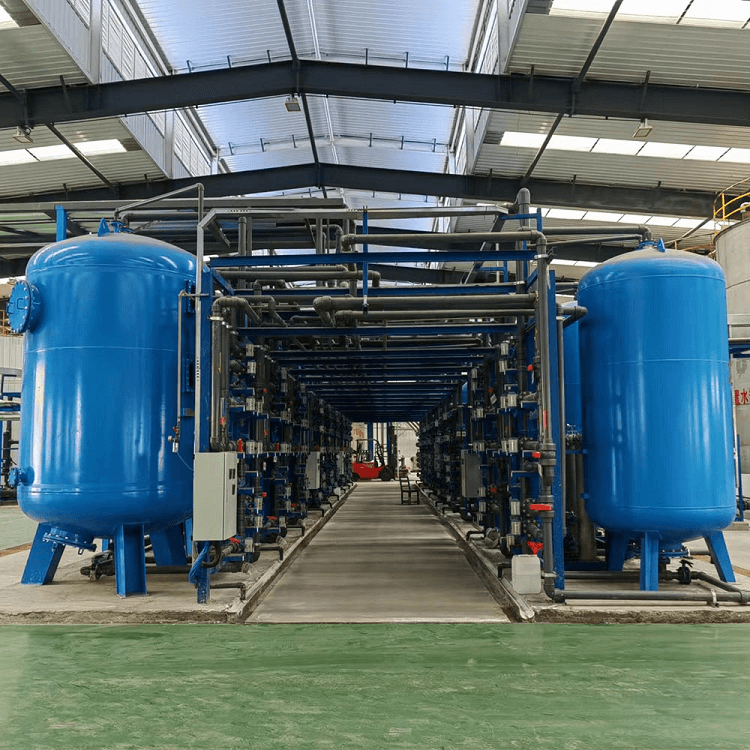

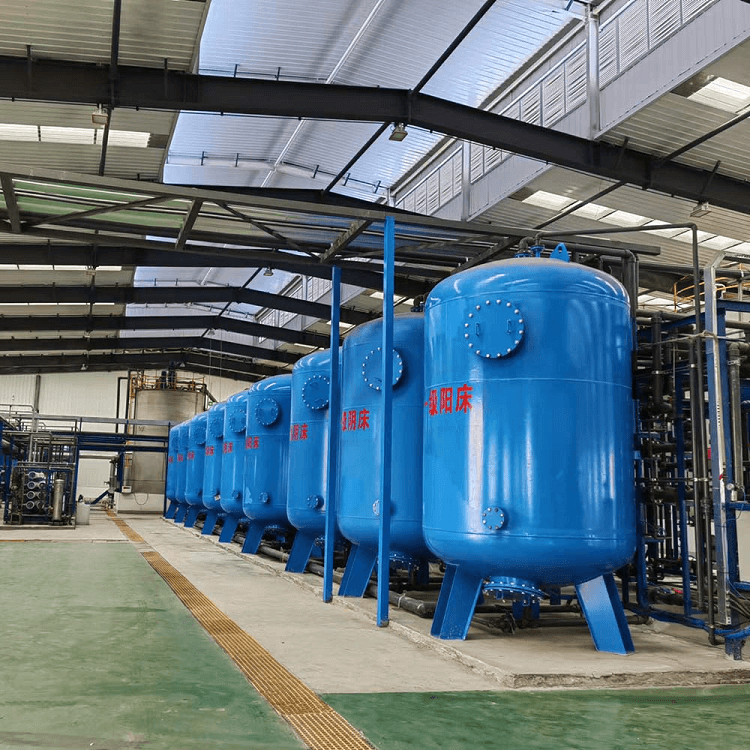
Hard Water Softener Filter System, water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water
Hinada can provide the integrated Water Solution according to client's project requirement.
Hard Water Softener Filter System, water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. Water softening is usually achieved using lime softening or ion-exchange resins but is increasingly being accomplished using nanofiltration[citation needed] or reverse osmosis membranes.

Water Softener Filtration Systems, Ion exchange resins, in the form of beads, are a functional component of domestic water softening units Conventional water-softening appliances intended for household use or Industry purpose depend on an ion-exchange resin in which "hardness ions"—mainly Ca2+ and Mg2+—are exchanged for sodium ions. ion-exchange devices reduce the hardness by replacing magnesium and calcium (Mg2+ and Ca2+) with sodium or potassium ions (Na+ and K+)."

Ion-exchange resins are organic polymers containing anionic functional groups to which the divalent cations (Ca2+) bind more strongly than monovalent cations (Na+). Inorganic materials called zeolites also exhibit ion-exchange properties. These minerals are widely used in laundry detergents. Resins are also available to remove the carbonate, bicarbonate, and sulfate ions that are absorbed and hydroxide ions that are released from the resin.
When all the available Na+ ions have been replaced with calcium or magnesium ions, the resin must be recharged by eluting the Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions using a solution of sodium chloride or sodium hydroxide, depending on the type of resin used. For anionic resins, regeneration typically uses a solution of sodium hydroxide (lye) or potassium hydroxide. The waste waters eluted from the ion-exchange column containing the unwanted calcium and magnesium salts are typically discharged to the sewage system Recharge typically takes the following steps:
Backwash: Water is directed through the resin in the opposite direction as normal flow, and the output is sent to a drain for disposal. This 10-minutes process flushes out solids and expands the resin bed.
Brine draw: Water is directed through a jet pump, which pulls salt water from the brine tank, before the water and brine pass through the resin bed in the normal direction, if co-current, or in the reverse direction, if counter current. The output of this typical 30 minute process is discarded through the drain hose.
Rinse: Brine draw stops, but water continues to flow from the inlet to the outlet, gradually flushing the brine out of the resin bed. The flushing water flows slowly for several minutes, then at a faster rate for as long as an hour. At some point, the brine reservoir is refilled with fresh water.